User:John07/wegbeschaffenheit/en
Tracktype
Used to describe the surface quality of the track, path or road.
| Key | Value | Element | Comment | Rendering | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tracktype | grade1 | Solid[1]. Usually a paved surface (called also |
|||
| tracktype | grade2 | Mostly solid. Usually an unpaved track with surface of gravel mixed with a varying amount of sand, silt, and clay. See Gravel road on Wikipedia. May be applicable to heavily degraded and crumbled roads which were paved in past. Often also tagged with surface=gravel;compacted;fine_gravel etc. |
|||
| tracktype | grade3 | Even mixture of hard and soft materials. An unpaved track. |
|||
| tracktype | grade4 | Mostly soft. An unpaved track prominently with soil/sand/grass, but with some hard or compacted materials mixed in. |
|||
| tracktype | grade5 | Soft. An unimproved track lacking hard materials, uncompacted, with surface of soil/sand/grass. |
|||
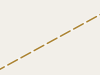
| tracktype | <no value> | If no tracktype tag is present, the track is rendered with a dot-dash line style (as shown right). |
This table is a wiki template with a default description in English. Editable here.
Smoothness
| Key | Value | Element | Usable by | Description | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| smoothness | excellent | (thin_rollers) roller blade, skate board and all below | As-new asphalt or concrete, smooth paving stones with seamless connections, etc. | 
| |
| smoothness | good | (thin_wheels) racing bike, sport motorcycles and all below | Asphalt or concrete showing the first signs of wear, such as narrow (<1.5 cm) cracks, wider cracks filled up with tar, shallow dents in which rainwater may collect, etc. that may cause trouble for rollers but not for racing bikes. The best roads paved with bricks, sett, etc. also fall in this category. | 
| |
| smoothness | intermediate | (wheels) city bike, sport cars, wheel chair, cruiser/touring motorcycles, Scooter and all below | Asphalt and equivalent that shows signs of maintenance such as patches of repaired pavement, wider cracks (>2 cm), etc. that may cause trouble for racing bikes. The pavement may contain potholes, but these are small, shallow (<3cm deep) and few so they are easily avoided, or the road shows damage due to subsidence (depressions of a scale >50 cm) or heavy traffic (shallow ruts in asphalt caused by trucks in summer). The quality of the surface starts to affect the speed of most passenger cars, so they will slow down to make the ride more comfortable (but still above 50% of the speed they would drive at if the road was smooth). The best unpaved but compacted roads fall in this category. | 
| |
| smoothness | bad | (robust_wheels) trekking bike, normal cars, commuter/standard motorcycles, Rickshaw and all below | Heavily damaged paved roads that badly need maintenance: many potholes, some of them quite deep. The average speed of cars is less than 50% of what it would be on a smooth road. However, it isn’t so rough that ground clearance becomes a problem. A ground clearance of a normal passenger car (>14 cm) is sufficient. Good unpaved roads without risk of damage to normal passenger cars are also included here. |  
| |
| smoothness | very_bad | (high_clearance) Car with high clearance, light-duty off road vehicles, adventure motorcycles (>180kg) | Unpaved roads with potholes and ruts, but still passable with an average SUV with a ground clearance of at least 18 cm.* | 
| |
| smoothness | horrible | (off_road_wheels) heavy-duty off road vehicles, dual-sport motorcycles (< 180kg) and all below | Unpaved tracks with ruts, rocks etc that need a ground clearance of at least 21 cm (Toyota Landcruiser, Landrover, Lada Niva, bukhanka, etc.). Skid plate protection is advisable. | 
| |
| smoothness | very_horrible | (specialized_off_road_wheels) tractor, ATV, tanks, Trial/Enduro motorcycles (<130kg), Mountain bike and all kind of off-highway vehicles (see also mtb:scale=*) | Tracks with deep ruts and other obstacles that need a ground clearance of at least 24 cm. | 
| |
| smoothness | impassable | No wheeled vehicle | Ways, often highway=path, that are not passable by any vehicles, not even mountain bikes or specialised off-road vehicles, but are recognisable in the landscape and may still be useful for hikers. Consider also lifecycle prefixes disused:*=* or abandoned:*=* if the way used to be a passable road but has deteriorated. | 
|
Please note: Photos are examples ONLY! The smoothness of a way should be assessed solely based on whether the way is usable by the vehicles mentioned above. A user of a certain road or path is only interested in whether the road can be driven or not. *Note that some unpaved tracks can be so steep that a car designed mostly for on-road use does not have the gear ratios and engine power needed to drive up a slope slow enough not to cause damage without the engine stalling. The track may still be smooth enough that such cars can drive down that slope without problem, so in such cases the track should be marked bad but the steep section tagged with incline=*.
This table is a wiki template with a default description in English. Editable here.
Surface
The surface tag is used in association with other tags, such as highway=* or leisure=pitch to provide additional information about the material with which the element is covered. See Landcover for a broader discussion of surfaces and landcover.
| Value | Comment | Photo | Abundance |
|---|---|---|---|
↑ ↓
Paved | |||
| paved | A feature that is predominantly paved; i.e., it is covered with paving stones, concrete or bitumen. This value gives general description; use a more precise value if possible, like asphalt, concrete, paving_stones and other options below. | 
|
|
| asphalt | Short for asphalt concrete - mineral aggregate bound by asphalt. | 
|
|
| chipseal | Less expensive alternative to asphalt concrete, using a thin base of hot bitumen or asphalt with aggregate pushed into it. Common in many American countries and Oceania. Often hard to distinguish from asphalt concrete by laypersons, some consider it as subtype of asphalt rather separate surface. In the end vast majority of chipsealed roads are tagged as surface=asphalt instead. | 
|
|
| concrete | Portland cement concrete, forming a large surface, typically cast in place and may have predetermined breaking joints. For pre-fabricated plates, please use concrete:plates or concrete:lanes if you know how the concrete is laid out and one of these tags fits. | 
|
|
| concrete:lanes | Long, narrow concrete elements for a two-tracked vehicle (motorcars) so that the tires always hit the concrete. There might be sand, ground, grass, pavers, asphalt, etc. in between them. Note that if you tag a single-tracked way you just use concrete, since there are no lanes. | 
|
|
| concrete:plates | Heavy duty concrete plates placed closely together. Might have tar, sand, or grass in between the connections. | 
|
|
| paving_stones | A relatively smooth surface paved with artificial blocks (block pavers, bricks) or natural stones (specifically, flagstones), with a flat top. The gaps between individual paving stones are very narrow, either because the stones have a perfectly regular shape (rectangular, or any surface-filling shape) or because they have been carefully selected, fitted and placed in order to form an even, closed surface. |  ] ]
|
|
| paving_stones:lanes | lanes of paving stones for two-tracked vehicles (motorcars). There might be sand, ground, grass, pavers, asphalt, etc. in between them. Note that if you tag a single-tracked way you just use paving_stones, since there are no lanes. | 
|
|
| grass_paver | A sort of permeable paving using regular cell structure, where the voids in this structure enable rainwater to drain into the ground and the structure itself increases the load bearing capability. Often used for parking lots or infrequently used service ways. | 
|
|
| sett | Sett paving, formed from natural stones cut to have roughly a flat top, with a regular or irregular shape. The stones do not cover the surface completely, unlike paving_stones. They also may be not entirely flat. |  
|
|
| unhewn_cobblestone | Raw cobblestone of natural, uncut, rounded stones. Unlike pebblestone, the stones are firmly connected to the ground. | 
|
|
| cobblestone | cobblestone is an unclear value, and was widely used for sett and actual cobblestone. Please adopt a more precise value, like sett or unhewn_cobblestone (described above). | ||
| Should not be used, as there is neither a commonplace or defined meaning. Likely use sett or unhewn_cobblestone instead. | |||
| bricks | A surface paved with dried clay bricks. Note that some people use surface=paving_stones for them and treat them as subtype of paving stones. | 
|
|
| metal | Used for metal-surfaced bridges, or for temporary tracks over fields for normal road vehicles or site traffic (note that objects lasting for just a few days should not be mapped in OSM).
Not used for road metal in the sense of crushed, quarried rock. |
 
|
|
| metal_grid | Metal grids are often used as a surface on industrial-style bridges or stairs. When wet, the surface can become very slippery, especially for bikes. The surface can also be unsuitable for dogs, due to the sharp edges and the look-through effect. This surface is sometimes known as metal grate, metal grating, steel grate/grating, or open grate. | 
|
|
| wood | Used for wood surfaced bridges, plank walkways, and garden decking. | 
|
|
| stepping_stones | Stones or plates individually arranged in a row, allowing to walk on, surrounded by an unpaved medium such as grass or water |  
|
|
| rubber | Playground safety surfacing made of recycled rubber tire products such as poured rubber, rubber tiles or loose rubber mulch. These surfaces are usually made of rubber designed specifically for aesthetics, child safety, and/or ADA wheelchair accessibility. | 
|
|
| tiles | Ceramic tiles. Those are commonly used for paving indoor corridors in public spaces such as airports or shopping malls. Outdoors, they are sometimes encountered on smaller footways in parks and terraces. | 
|
|
| fibre_reinforced_polymer_grate | Oftern used on outdoor walkways, they provide good grip due to the rough surface and open grate allows water to go through the surface. Also known as FRP Grate/Grating. | 
|
|
| user_defined | All commonly used values according to Taginfo. | ||
Unpaved | |||
| unpaved | A feature that is predominantly unsealed (unpaved); i.e., it has a loose covering ranging from compacted stone chippings to soil. Unpaved roads may, in aerial imagery, show evidence of water along their course; in such circumstances, the waterway should not be tagged as a stream, though it might appear as such. This value gives only a rough description; use a more precise value if possible. | ||
| compacted | A mixture of larger (e.g., gravel) and smaller (e.g., sand) parts, compacted (e.g., with a roller), so the surface is more stable than loose gravel. Used, for example, for park paths, better tracks, some service ways, … Best sort of ways below paving with asphalt, concrete, paving stones. Sometimes known as water-bound macadam. Mixture and compacting leads to more grip and stability. | 
|
|
| fine_gravel | This tag is used somewhat inconsistently; see its detail page. It may be used to specify fine loose gravel (as shown in the picture) which makes it unsuitable for road bicycles, but it is also sometimes used as an alias for compacted, which is easy to cycle on. If the gravel is fixed instead of loose, please consider using well-defined compacted instead. | 
|
|
| gravel | This tag has very large meaning range. Used for cases ranging from huge gravel pieces like track ballast used as surface, through small pieces of gravel to compacted surface. | 
|
|
| shells | Crushed or whole seashells; commonly seen on footways and cycleways in the Netherlands. | 
|
|
| rock | Big pieces of rock used to improve path quality or exposed bare rock, including trails across natural=bare_rock. Typically in mountainous areas. |  
|
|
| pebblestone | Pebbles are stones rounded by waves or river flow. Typical size range from 2 to 8 cm. Describing a surface in OSM they are loosely arranged. Like gravel pebbles can be used as a building part of compacted. | 
|
|
| ground | No special surface, the ground itself has marks of human or animal usage. This value gives only a rough description; if possible, use a more precise value such as grass, clay, sand, dirt, gravel or pebblestone. | 
|
|
| dirt | Used for where surface is exposed soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, but it is not sand, gravel, or rock. Gravel is sometimes mistakenly called dirt. Some compacted surfaces are sometimes called "dirt" too, please consider the definition of compacted. | 
|
|
| earth | The same meaning as dirt. Use the more common dirt instead. | 
|
|
| grass | Grass covered ground. Mostly nice to walk. May turn into surface=dirt or become overgrown and disappear. | 
|
|
| mud | Similar to ground but most of the year wet which gives a soft ground with low carrying capacity. Mostly found on wetland like swamps or in tidal areas. Sometimes also found on slopes draining onto a way. | 
|
|
| sand | Small to very small fractions (less than 2 mm) of rock. | 
|
|
| woodchips | Woodchips as a surface, perhaps for a playground or walking trail. Can consist of either chips of actual wood, or of bark only. Sometimes written as wood chips. | 
|
|
| snow | Winter roads surfaced with compacted snow. | 
|
|
| ice | Ice roads, winter roads | 
|
|
| salt | Dry salt lakes | 
|
|
| user_defined | All commonly used values according to Taginfo. | ||
Special (sports, etc.) | |||
| clay | Most common on tennis courts. Sometimes used for other sports: soccer, athletic tracks, boules, etc. | 
|
|
| tartan | A synthetic, all-weather surface typically used in running and other sport tracks. Although Tartan is a trademark, it is used as a generic term due to its widespread usage. Other well-known brand names include Rekortan or Mondotrack. | 
|
|
| artificial_turf | An all-weather surface made from synthetic fibres to look and feel like natural grass. Often used for tracks and pitches of sports such as football, baseball, etc. | 
|
|
| acrylic | An artificial surface covered with acrylic resin-bound coating. Often used for tennis courts, basketball courts, etc. Prominent brands include: DecoTurf, GreenSet and so on. | 
|
|
| carpet | Carpet may be used for some sport courts such as indoor tennis courts and appear on some highway=corridor. | 
|
|
| plastic | An artificial surface made from plastic, can be used on pitches and playgrounds. | 
|
|
| user_defined | All commonly used values according to Taginfo. | ||
This table is a wiki template with a default description in English. Editable here.