OpenRailwayMap/Tagging in Belgium
This tagging scheme is a work in progress. As such, it's best to not translate it to other languages yet.
Tracks
General
General tags in Belgium are:
- operator=* in general operator is Infrabel. On industrial lines and heritage lines, this may not be true.
- ref=* name of the railway line, i.e. ref=L162
- usage=* for example usage=main
Gauge
The Belgian railways use the standard track gauge.
- gauge=1435
Electrification systems
The following electrification systems are used in Belgium:
Non-electrified
- electrified=no
DC electrification
- electrified=contact_line
- voltage=3000
- frequency=0
AC electrification
- electrified=contact_line
- voltage=25000
- frequency=50
Train protection
- railway:tbl=yes TBL train protection
- railway:tbl=1+ TBL1+ train protection (remark: railway:tbl=2 is possible, but TBL2 is discontinued and line 2 is now equipped with ETCS)
- railway:etcs=yes European Train Control System
- railway:etcs=1 ETCS Level 1 – Trackside signals are equipped with Eurobalises that transmit i.a. the state of the signal
- railway:etcs=2 ETCS Level 2 – The state of signals is transmitted over a GSM-R link. Eurobalises only transmit static information, such as line speed, curves and distance to the next balise. Trackside signals are optional (exclusive cab signalling is possible)
Milestones
These are mapped as ![]() nodes on the railway line:
nodes on the railway line:
- railway=milestone
- railway:position=*: value in km, decimals separated with "."
- railway:milestone:catenary_mast=yes/no: whether the milestone sign is mounted on a catenary mast
Signalling

- railway=signal
- railway:signal:main=BE:GSA
- railway:signal:direction=backward (the way should be drawn in the direction towards the camera)
- railway:signal:position=left
- railway:signal:speed_limit=BE:VIS
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=light
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=50 (possibly also others, this is not visible on the image)
 To do: a tag for the chevron on top still has to be invented
To do: a tag for the chevron on top still has to be invented - ref=CX-D.45
The main tag for any type of signal, whether light or sign, is railway=signal.
Light signals have an identification sign with the name of the signal, which can be mapped with
![]() To do: tag for signals mounted higher than normal on a gantry or catenary mast, probably with a new value for
To do: tag for signals mounted higher than normal on a gantry or catenary mast, probably with a new value for railway:signal:*:height=*
Main signal
FR: grand signal d'arrêt, NL: groot stopsein
Signalling in Belgium is relatively simple, because the signals and distant signals have the same shape. The main signals, "big stop signals", have a white rectangular identification plate. Distant signals look almost identical but have a round yellow identification plate (see below). Most big stop signals can also show the aspects of distant signals: they can act as a stop signal and distant signal in one.
(You can learn what these aspects mean at several websites, such as railpassion.eu (FR), railpassie.eu (NL) or cooltrain.be (NL)
Regime
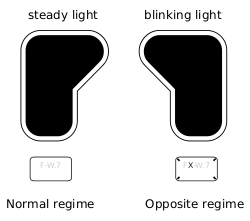
(FR: régime de voie normale / régime de contre-voie, NL: regime normaalspoor / regime tegenspoor)
Trains in Belgium are either in "normal regime" or in "opposite regime". Shunting operation is always in normal regime.
The form of big signals reflects the regime of trains that see it, see the drawing on the right or above.
From the point of view of the driver, by default normal regime signals are placed on the left side of the track, opposite regime signals on the right side. Exceptions to this are possible, in those cases a round blue sign with a white arrow points to the track the signal applies to.
In the vast majority of cases where there are 2 tracks next to each other, trains preferably drive on the left. On the left track, you will see exclusively normal regime signals and on the right track opposite regime signals.
While normally a track seems to have a canonical direction, this is not true in general: you can find big signals that are placed in opposing directions close by on the same track that are both normal regime.
Main tags
- railway:signal:main=BE:GSA where GSA is "grand signal d'arrêt" (NL: groot stopsein)
- railway:signal:main:form=light since this signal not a semaphore. Due to the fact that nearly all signals are lights, this tag can be skipped for reasons of data minimisation.
- railway:signal:main:states=BE:V/BE:VJH/BE:VJV/BE:2J/BE:RB/BE:R/BE:ECS-V/BE:ECS-U/BE:ECS-CAB/BE:ECS-TCS
- railway:signal:direction=forward/backward for which direction the signal applies to, relative to the direction of the OSM way.
- railway:signal:regime=normal/opposite (See Regime above.)
- railway:signal:position=left/right with regard to the direction of the OSM way. For backward facing signals, this is the inverse of the side that the train driver sees the signal at.
With distant speed limit indicator
![]() To do: chevron (changement de régime); répere de voie en impasse
To do: chevron (changement de régime); répere de voie en impasse
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=BE:ARV advance speed limit, displayed with a yellow number above the main signal image (annonce de reduction de vitesse, nombre jaune)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=light
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=* value of the indicated speed limit in km/h, can be multiple values as well: 40; 60; 100. You can often see what possibly values there are by looking at how the little lamps are arranged, even if they aren't on.
With speed limit indicator
- railway:signal:speed_limit=BE:VIS applies, if a speed limit is added below the main signal image (vitesse imposé par le signal)
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=light/sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=* value of the indicated speed limit in km/h, can be multiple values as well: i.e. 40; 60; 100
With ETCS zone start/end sign
These signs are mainly installed on stop signals, but can sometimes be installed as stand-alone signs.
Start of ETCS Level 1 Limited Supervision zone
- railway:signal:train_protection=BE:ETCS-1LS
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=start
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
Start of ETCS Level 1 Full Supervision zone
- railway:signal:train_protection=BE:ETCS-1FS
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=start
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
Start of ETCS Level 2 Full Supervision zone
- railway:signal:train_protection=BE:ETCS-2
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=start
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
End of ETCS zone
- railway:signal:train_protection=BE:ETCS-end
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=end
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
Distant signal
FR: signal avertisseur, NL: verwittigingssein
Distant signals have a round yellow identification plate.
- railway:signal:distant=BE:SAI Signal Avertisseur Indépendant
- railway:signal:distant:states=BE:V/BE:VJH/BE:VJV/BE:2J
- railway:signal:regime=normal/opposite
- ref=* The SAI has the same reference as the repeated signal but in small letters.
Repeater
Repeaters show a horizontal line or a diagonal line depending on the state of a nearby signal that is hidden around a corner. They are much closer to their signal than a distant signal.
- railway:signal:main_repeated=BE:RTL Répétiteur à Traits Lumineux
- railway:signal:main_repeated:form=light
- ref=* The repeater has the same reference as the repeated signal.
Simplified stop signals
You will find these mostly within marshalling yards, but they apply to all movements.
- railway:signal:minor=BE:SAS where SAS means "signal d'arrêt simplifié" (NL: vereenvoudigd stopsein)
- railway:signal:shunting:height=dwarf/normal, whether the signal is placed on the ground (dwarf) or if it's at normal height
Shunting signals
These only apply to small movement (shunting, first movement after changing driver, etc.)
- railway:signal:shunting=BE:PSA where PSA means "petit signal d'arrêt" (NL: klein stopsein)
- railway:signal:shunting:form=light/sign Small stop signs can be lights or signs (e.g. always closed, at a dead end), so this tag cannot be skipped as with the big stop signals.
Speed limits
The speed of a track is tagged with:
- maxspeed=*
The speeds are indicated at the trackside with a signs. As is common in the railway sector, those values should multiplied by 10 to arrive at the speed in km/h.
It is always necessary to add the direction of these signs:
- railway:signal:direction=forward/backward, relative to the direction of the OpenStreetMap way.
Note: if a sign has two dots on it, it's a temporary sign and should not be mapped! Example: ![]()
Reference speed
- railway:signal:speed_limit=BE:PVR panneau vitesse réference
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=* speed indicated by the sign (×10 km/h)
Announcement of a speed limit
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=BE:PVA panneau d'annonce
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=*
Beginning of a speed limit
- railway:signal:speed_limit=BE:PVO panneau d'origine
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=*
New, higher limit, below the reference speed
- railway:signal:speed_limit=BE:PVJ panneau "fin de zone" jaune à bord vert
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=*
New, higher limit for some traffic
- railway:signal:speed_limit=BE:PVV panneau "fin de zone" vert à bord jaune
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=*
This is the least common speed sign. It is placed between an ![]() announcement sign and and an
announcement sign and and an ![]() origin sign after a line where a lower speed limit was in effect joins. The trains coming from that line may increase their speed when passing this sign. For drivers who had passed the
origin sign after a line where a lower speed limit was in effect joins. The trains coming from that line may increase their speed when passing this sign. For drivers who had passed the ![]() announcement sign, this sign does not apply: they have to attain the lower speed only at the
announcement sign, this sign does not apply: they have to attain the lower speed only at the ![]() origin sign.
origin sign.
Lines with stop markers
These markers are used to mark stop positions on lines where only cab signalling is used. Whether the train is allowed to pass them, is displayed on a display in the train's cab.
Stop markers
The stop markers can be tagged similar to the Netherlands:
- railway:signal:train_protection=BE:PRA Panneau Repère d'Arrêt
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=block_marker
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
- Depending on the shape of the stop marker:
Traction
Contact line segmentation
- railway:signal:electricity=BE:SLC Sectionnement Ligne de Contact
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:catenary_mast=yes/no
End of contact line
- railway:signal:electricity=BE:FLC Fin de Ligne de Contact
- railway:signal:electricity:type=end_of_catenary
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
Panto distant
- railway:signal:electricity=BE:PBA Panto baisser annonce
- railway:signal:electricity:type=pantograph_down_advance
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
Panto down
- railway:signal:electricity=BE:PBE Panto baisser execution
- railway:signal:electricity:type=pantograph_down
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
Panto up
- railway:signal:electricity=BE:PRL Panto relever
- railway:signal:electricity:type=pantograph_up
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign